Periodontitis and Teeth Health: A Complete Overview of the Gum Disease

Everyone knows they should brush their teeth twice a day and floss at least once daily (↗) to keep their teeth and gum healthy. But not everyone flosses as much as they should, leading them to have gum or periodontal disease.
At the initial stage, the disease often presents as mere inflammation of the gums, better known as gingivitis. Most people usually do not take it seriously, but they should. If left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss or more severe health issues.
So, here is all you need to know about how to manage gum disease before it worsens.
Gum Disease Starts with Bacteria
Before you schedule your next appointment with the dentist, you should understand that bacteria are the root cause of gum disease, including gingivitis. Although our mouth is normally full of bacteria, they mostly serve the positive function of maintaining a healthy PH balance. However, it doesn’t take much for these bacteria to start harming our health.
Over time, plaque can build up on your teeth if you’re not cleaning them properly. Hardened plaque becomes tartar, which increases the chances of gingivitis forming; this is the precursor to gum disease.
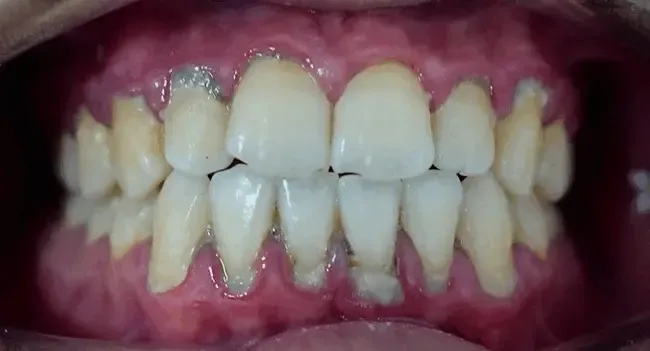
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a severe form of gum disease. This condition makes your gums pull away from the teeth, causing bone loss. The teeth may eventually fall out or become loose.
The formation of tartar in the teeth and gums is the likely reason for periodontitis. Initially, pockets form underneath the loosened teeth. Tartar can get trapped in these pockets and force your body to fight off the infection.
If left untreated for too long, your body will start to attack the bone at the base of your teeth, which can result in them getting loose and falling out.
How To Spot Gum Disease
✅ The best way to spot gum disease is to check your teeth regularly and spot it in its earliest stages. There are some specific signs you can look out for:
✅ One of the first main ones is persistent bad breath. If you notice bad breath even after you haven’t eaten anything for a while or you brushed your teeth, you could be in the early stage of gum disease.
✅ A second sign you can look out for is swollen gums. As the gums start pulling away from the teeth, they become swollen due to bacterial infection.
✅ A third sign to look out for is painful chewing. The soft tissues of your mouth become inflamed because of an infection, and this can result in some pain.
✅ Lastly, check to see if you have loose teeth. It might be a little late, but that doesn’t mean you should give up. Make an appointment with your dentist as soon as you notice this. There is a possibility that you may still save your teeth and reverse most of the damage.
What Preventative Measures Can You Take to Prevent Gum Disease?
Other than cleaning your teeth and flossing regularly, there are some activities you should avoid.
Avoid smoking. Smoking should be the first thing you avoid. Gum disease is more likely to develop if you smoke. It may even make your gum disease worse and more challenging to treat.
Other risk factors include certain prescription medications, diabetes, and other illnesses that affect teeth and gums. So, you should immediately seek advice from your dentist if you have any of the known risk factors. They will let you know how you can prevent it from happening.
Recommended Reading:
What Are the Treatment Options for Gum Disease?
Treatment options for gum disease largely depend on its severity and extent. Early on, your dentist might go for a deep clean to get rid of all the tartar and plaque in those affected areas.
So, make sure to swing by your dentist's clinic. They've got you covered. But remember, once you're home, keeping up with the cleaning is all on you. The best way to keep your teeth and gums in tip-top shape? Brushing and flossing regularly. Doing these consistently can stop plaque and tartar from building up again.
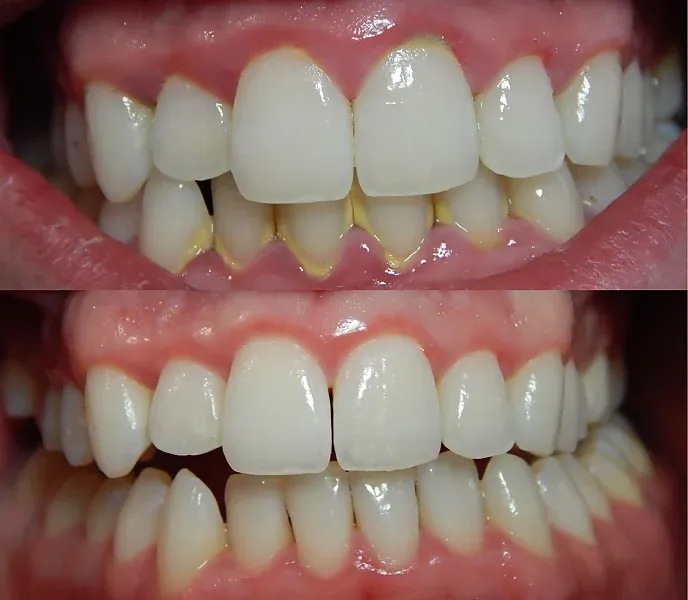
Medication and surgery are typically the better options when a deep cleaning treatment is inadequate to address the problem. You should consult with your dentist to see which medications can be helpful, given the severity of your case.
If your dentist recommends surgery, you should ask about the pros and cons of the surgery so that you know what to expect. Surgery is never something you should undertake lightly. But it might be your best option, especially if you have an advanced case of gum disease.
When Should You Visit Your Dentist?
If you believe that you are starting to develop gum disease or would like a dental appointment to have your mouth examined to put your mind at ease, then you shouldn’t wait to visit your dentist’s office. The earlier your dentist examines your case, the better chance you will have to address the problem before it worsens.
And even after your appointment, you should be more careful with your dental hygiene at home. Also, get regular checkups and cleanings to prevent it from recurring.
Final Thoughts
Caring for your teeth and gums also contributes to maintaining the rest of your health. The gum infection may affect other parts of your body via the bloodstream. Additionally, ongoing pain and swelling can severely affect the heart, causing tiny blood clots to lodge in the valves and potentially causing heart attacks or strokes.
So be sure to make a dental appointment with your regular dentist or, if you don’t have one, schedule an appointment with the dentist nearest you as soon as possible.
About This Article
This article is sponsored by Northstar dental care of Nazareth (↗). It was medically reviewed by Dr. Adeel Ali, an accomplished implant dentist with a diploma from the prestigious Royal College of Surgeons of England. He is a UK-based practitioner, trainer, and international speaker. His speciality lies in sinus grafting and transformative dentistry.
- BruceBlaus, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
- Onetimeuseaccount, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
- Shaimaa Abdellatif, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons


